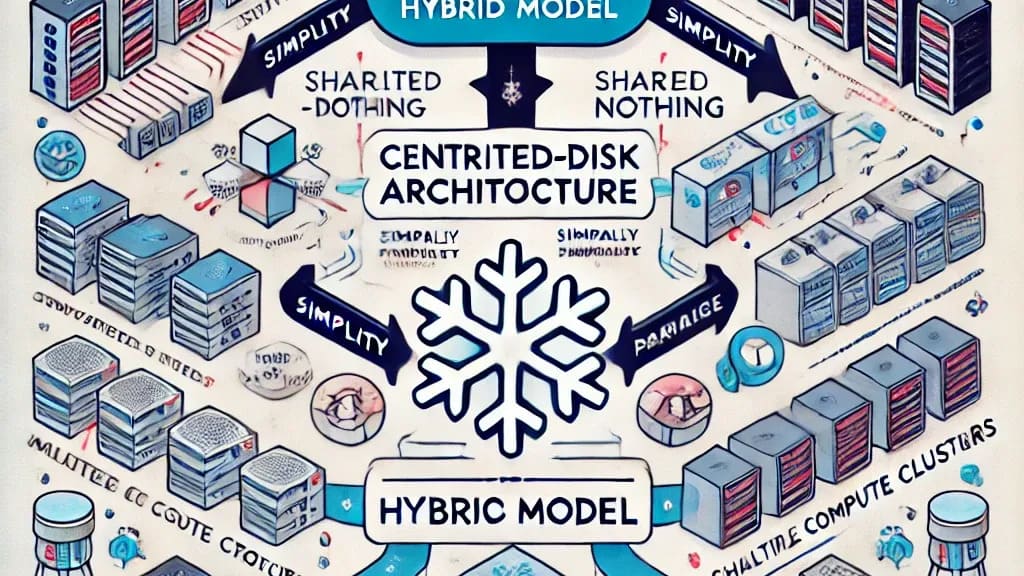
In the dynamic world of data warehousing, Snowflake stands out with its innovative hybrid architecture, blending the best elements of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing database models. This architectural design isn’t just a clever technical feat—it’s the cornerstone of Snowflake’s ability to deliver simplicity, scalability, and stellar performance.
The Hybrid Model: A Perfect Fusion
Snowflake’s architecture cleverly integrates two traditional database paradigms:
- Shared-Disk Architecture:
- In a shared-disk model, all compute nodes access a central repository for persisted data.
- Snowflake emulates this by maintaining a centralized data repository accessible to all compute nodes. This centralization simplifies data management, as all nodes in the system share a single source of truth.
- Shared-Nothing Architecture:
- The shared-nothing model distributes data and processing across independent nodes, each responsible for its own subset of the data.
- Snowflake leverages this by using Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) compute clusters. Each node in the cluster processes a portion of the dataset, enabling high-performance query execution.
Why Hybrid? The Best of Both Worlds
By combining these two architectures, Snowflake achieves a remarkable balance:
- Simplicity of Shared-Disk:
- Centralized data storage means administrators don’t have to deal with complex replication or synchronization issues across nodes.
- All nodes access the same persisted data, making Snowflake easy to use and maintain.
2. Performance of Shared-Nothing:
- The use of MPP compute clusters allows Snowflake to distribute queries across multiple nodes.
- This scale-out capability enables Snowflake to handle massive workloads efficiently, making it highly performant and cost-effective.
Key Benefits of Snowflake’s Hybrid Architecture
- Scalability:
- Need more power? Simply add more compute nodes. Snowflake’s architecture enables seamless horizontal scaling, accommodating workloads from small teams to global enterprises.
2. Concurrency:
- Unlike traditional systems that might struggle under heavy user loads, Snowflake’s compute clusters ensure multiple users and workloads can run simultaneously without performance bottlenecks.
3. Simplicity:
- The centralized data repository eliminates many of the complexities associated with managing distributed systems.
- Administrators can focus on strategic tasks rather than troubleshooting synchronization issues.
4. Elasticity:
- Snowflake’s compute and storage layers are decoupled, allowing users to scale resources independently based on workload demands.
Hybrid Architecture in Action
Imagine a company running complex analytics on terabytes of e-commerce data. With Snowflake:
- Centralized Data: All e-commerce data is stored in Snowflake’s central repository, ensuring consistent and reliable access.
- Parallel Query Execution: When a user queries purchase trends, Snowflake’s compute nodes collaborate to process the data in parallel, delivering results in seconds.
- Scalable Power: As the company grows and data volumes increase, they can add more compute nodes to handle the load seamlessly.
Conclusion: The Future of Data Warehousing
Snowflake’s hybrid architecture is more than just a technical innovation—it’s a game-changer in data warehousing. By blending the simplicity of shared-disk models with the scalability of shared-nothing systems, Snowflake delivers a platform that’s not only powerful but also intuitive to use. This unique approach positions Snowflake as a leader in the data warehousing space, enabling businesses to unlock the full potential of their data with ease and efficiency.
In a world where data-driven decisions drive success, Snowflake’s hybrid architecture is the secret weapon businesses need to thrive.


Ustas
Hey, not always needs to be add the nodes, sometimes you can add cluster on warehouse and your task will be good.