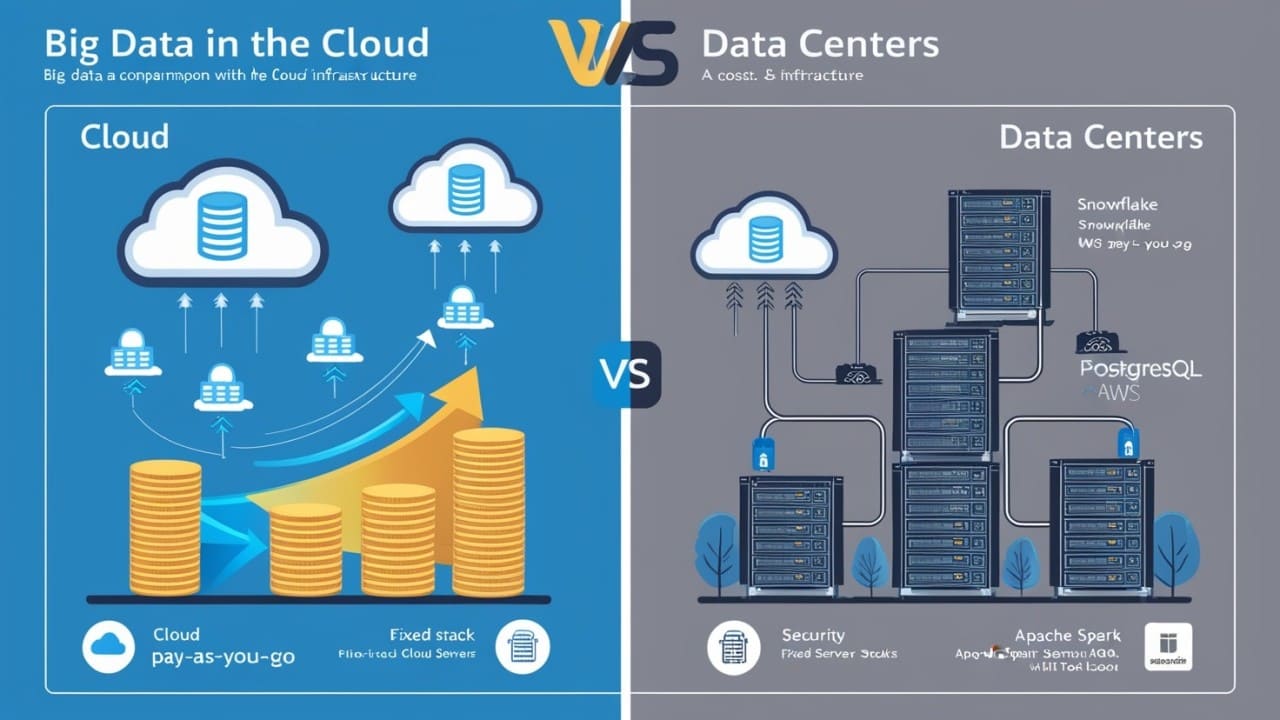
Big Data in the Cloud vs. Data Center: What’s Cheaper, What’s Better?
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of managing and processing Big Data, a crucial decision remains: should you leverage the flexibility of the cloud or stick with the control of an on-premises data center? Each approach offers distinct advantages and trade-offs, and the right choice depends heavily on your organization’s needs and priorities.
Cost Considerations: Cloud vs. Data Center
Cloud Costs
- Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure operate on flexible pricing models, allowing organizations to pay only for the resources they use.
- Operational Expenses: Cloud solutions reduce upfront capital expenditure (CapEx) but may incur higher operational costs over time, especially for sustained workloads.
- Hidden Costs: Data egress fees, over-provisioned resources, and lack of cost monitoring can lead to unexpectedly high bills.
Data Center Costs
- Upfront Investment: Data centers require significant CapEx for hardware, infrastructure, and setup.
- Predictable Expenses: Once established, on-premises solutions often result in stable operational costs.
- Maintenance Overhead: Organizations must budget for hardware maintenance, upgrades, and staffing.
Performance and Scalability
Cloud
- Elastic Scalability: Cloud platforms excel at handling fluctuating workloads, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Global Reach: Distributed cloud infrastructure reduces latency for globally dispersed teams and applications.
Data Center
- Consistent Performance: On-premises systems are designed for predictable workloads and low latency for internal applications.
- Scaling Limitations: Scaling on-premises systems requires significant planning, investment, and time.
Data Security and Control
Cloud
- Shared Responsibility Model: Cloud providers secure the infrastructure, but customers are responsible for securing their data.
- Compliance Challenges: Data sovereignty laws can complicate cloud adoption for sensitive datasets.
Data Center
- Full Control: On-premises systems allow organizations to manage their data and infrastructure entirely.
- Better for Sensitive Data: Data centers are ideal for businesses with stringent compliance and security requirements.
Flexibility and Innovation
Cloud
- Rapid Deployment: Cloud platforms enable quick provisioning of resources, speeding up innovation cycles.
- Tool Ecosystems: Integrated services for AI, ML, and analytics streamline advanced workflows.
Data Center
- Customization: On-premises systems offer deep customization but often require greater technical expertise.
- Slower Innovation: The time required for upgrades and new installations can hinder rapid development.
Conclusion: Which One is Right for You?
The choice between cloud and data center solutions ultimately depends on your organization’s priorities:
- Choose the Cloud if: You prioritize flexibility, scalability, and rapid innovation, and can manage ongoing operational costs effectively.
- Choose a Data Center if: You need complete control over your data, have predictable workloads, or must comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
Many organizations find success with hybrid solutions, combining the scalability of the cloud with the reliability of on-premises systems.
Comprehensive List of Tools
Cloud Tools
- Data Ingestion and Integration: AWS Glue, Google Dataflow, Azure Data Factory, Fivetran.
- Databases and Storage: Amazon RDS, Snowflake, BigQuery, DynamoDB, Amazon S3.
- Data Processing and Analytics: Databricks, AWS EMR, Google Dataproc, Azure Synapse Analytics.
- BI and Visualization: Tableau Online, Google Looker, Power BI (Cloud), QuickSight.
- Data Governance: AWS Lake Formation, Google Data Catalog, Azure Purview.
- Machine Learning: AWS SageMaker, Google Vertex AI, Azure ML Studio, DataRobot.
Data Center Tools
- Data Ingestion and Integration: Apache NiFi, Talend, Informatica PowerCenter.
- Databases and Storage: PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, Hadoop HDFS.
- Data Processing and Analytics: Apache Spark, Cloudera, Hadoop MapReduce, PrestoDB (On-Premises).
- BI and Visualization: Tableau (On-Premises), QlikView, SAP BusinessObjects, MicroStrategy.
- Data Governance: Apache Atlas, Informatica Axon, Erwin Data Modeler.
- Machine Learning: TensorFlow (On-Premises), H2O.ai (On-Premises), RapidMiner.
What is your organization’s strategy for managing Big Data? Are you leaning towards the cloud, on-premises solutions, or a hybrid approach? Share your thoughts in the comments below!



Leave a Reply